H5 和小程序拍照图片旋转、压缩和上传
2018年09月29日 05:33:10
最近接到一个“发表评论”的需求:用户输入评论并且可以拍照或从相册选择图片上传,即支持图文评论。需要同时在 H5 和小程序两端实现,该需求处理图片的地方较多,本文对 H5 端的图片处理实践做一个小结。项目代码基于 Vue 框架,为了避免受框架影响,我将代码全部改为原生 API 的实现方式进行说明,同时项目代码中有很多其他额外的细节和功能(预览、裁剪、上传进度等)在这里都省去,只介绍与图片处理相关的关键思路和代码。小程序的实现方式与 H5 类似,不再重述,在文末附上小程序端的实现代码。
拍照
使用<input>标签,type设为"file"选择文件,accept设为"image/*"选择文件为图片类型和相机拍摄,设置multiple支持多选。监听change事件拿到选中的文件列表,每个文件都是一个Blob类型。
<input type="file" accept="image/*" multiple />
<img class="preivew" />
<script type="text/javascript">
function onFileChange (event) {
const files = Array.prototype.slice.call(event.target.files)
files.forEach(file => console.log('file name:', file.name))
}
document.querySelector('input').addEventListener('change', onFileChange)
</script>注意:如果连续选择相同文件,第二次选文件不会触发
change事件,因为value值未发生变化,而<input>的change事件仅在value变化时触发。解决办法:在 change 事件处理方法中完成对文件的处理后重置value为默认值"",一旦 value 的值被重置,files的值也会同时被自动重置。
图片预览
URL.createObjectURL方法可创建一个本地的 URL 路径指向本地资源对象,下面使用该接口创建所选图片的地址并展示。
function onFileChange (event) {
const files = Array.prototype.slice.call(event.target.files)
const file = files[0]
document.querySelector('img').src = window.URL.createObjectURL(file)
}图片旋转
通过相机拍摄的图片,由于拍摄时手持相机的方向问题,导致拍摄的图片可能存在旋转,需要进行纠正。纠正旋转需要知道图片的旋转信息,这里借助了一个叫 exif-js 的库,该库可以读取图片的 EXIF 元数据,其中包括拍摄时相机的方向,根据这个方向可以推算出图片的旋转信息。
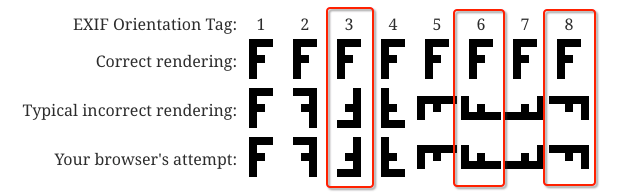
下面是 EXIF 旋转标志位(参考JPEG Orientation),总共有 8 种,但是通过相机拍摄时只能产生1、3、6、8 四种,分别对应相机正常、顺时针旋转180°、逆时针旋转90°、顺时针旋转90°时所拍摄的照片。
所以纠正图片旋转角度,只要读取图片的 EXIF 旋转标志位,判断旋转角度,在画布上对图片进行旋转后,重新导出新的图片即可。其中关于画布的旋转操作可以参考canvas 图像旋转与翻转姿势解锁这篇文章。下面函数实现了对图片文件进行旋转角度纠正,接收一个图片文件,返回纠正后的新图片文件。
/**
* 修正图片旋转角度问题
* @param {file} 原图片
* @return {Promise} resolved promise 返回纠正后的新图片
*/
function fixImageOrientation (file) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 获取图片
const img = new Image();
img.src = window.URL.createObjectURL(file);
img.onerror = () => resolve(file);
img.onload = () => {
// 获取图片元数据(EXIF 变量是引入的 exif-js 库暴露的全局变量)
EXIF.getData(img, function() {
// 获取图片旋转标志位
var orientation = EXIF.getTag(this, "Orientation");
// 根据旋转角度,在画布上对图片进行旋转
if (orientation === 3 || orientation === 6 || orientation === 8) {
const canvas = document.createElement("canvas");
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
switch (orientation) {
case 3: // 旋转180°
canvas.width = img.width;
canvas.height = img.height;
ctx.rotate((180 * Math.PI) / 180);
ctx.drawImage(img, -img.width, -img.height, img.width, img.height);
break;
case 6: // 旋转90°
canvas.width = img.height;
canvas.height = img.width;
ctx.rotate((90 * Math.PI) / 180);
ctx.drawImage(img, 0, -img.height, img.width, img.height);
break;
case 8: // 旋转-90°
canvas.width = img.height;
canvas.height = img.width;
ctx.rotate((-90 * Math.PI) / 180);
ctx.drawImage(img, -img.width, 0, img.width, img.height);
break;
}
// 返回新图片
canvas.toBlob(file => resolve(file), 'image/jpeg', 0.92)
} else {
return resolve(file);
}
});
};
});
}图片压缩
现在的手机拍照效果越来越好,随之而来的是图片大小的上升,动不动就几MB甚至十几MB,直接上传原图,速度慢容易上传失败,而且后台对请求体的大小也有限制,后续加载图片展示也会比较慢。如果前端对图片进行压缩后上传,可以解决这些问题。
下面函数实现了对图片的压缩,原理是在画布上绘制缩放后的图片,最终从画布导出压缩后的图片。方法中有两处可以对图片进行压缩控制:一处是控制图片的缩放比;另一处是控制导出图片的质量。
/**
* 压缩图片
* @param {file} 输入图片
* @returns {Promise} resolved promise 返回压缩后的新图片
*/
function compressImage(file) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 获取图片(加载图片是为了获取图片的宽高)
const img = new Image();
img.src = window.URL.createObjectURL(file);
img.onerror = error => reject(error);
img.onload = () => {
// 画布宽高
const canvasWidth = document.documentElement.clientWidth * window.devicePixelRatio;
const canvasHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight * window.devicePixelRatio;
// 计算缩放因子
// 这里我取水平和垂直方向缩放因子较大的作为缩放因子,这样可以保证图片内容全部可见
const scaleX = canvasWidth / img.width;
const scaleY = canvasHeight / img.height;
const scale = Math.min(scaleX, scaleY);
// 将原始图片按缩放因子缩放后,绘制到画布上
const canvas = document.createElement('canvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
canvas.width = canvasWidth;
canvas.height = canvasHeight;
const imageWidth = img.width * scale;
const imageHeight = img.height * scale;
const dx = (canvasWidth - imageWidth) / 2;
const dy = (canvasHeight - imageHeight) / 2;
ctx.drawImage(img, dx, dy, imageWidth, imageHeight);
// 导出新图片
// 指定图片 MIME 类型为 'image/jpeg', 通过 quality 控制导出的图片质量,进行实现图片的压缩
const quality = 0.92
canvas.toBlob(file => resolve(tempFile), "image/jpeg", quality);
};
});
},图片上传
通过FormData创建表单数据,发起 ajax POST请求即可,下面函数实现了上传文件。
注意:发送
FormData数据时,浏览器会自动设置Content-Type为合适的值,无需再设置Content-Type,否则反而会报错,因为 HTTP 请求体分隔符 boundary 是浏览器生成的,无法手动设置。
/**
* 上传文件
* @param {File} file 待上传文件
* @returns {Promise} 上传成功返回 resolved promise,否则返回 rejected promise
*/
function uploadFile (file) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 准备表单数据
const formData = new FormData()
formData.append('file', file)
// 提交请求
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open('POST', uploadUrl)
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (this.readyState === XMLHttpRequest.DONE && this.status === 200) {
resolve(JSON.parse(this.responseText))
} else {
reject(this.responseText)
}
}
xhr.send(formData)
})
}小结
有了上面这些辅助函数,处理起来就简单多了,最终调用代码如下:
function onFileChange (event) {
const files = Array.prototype.slice.call(event.target.files)
const file = files[0]
// 修正图片旋转
fixImageOrientation(file).then(file2 => {
// 创建预览图片
document.querySelector('img').src = window.URL.createObjectURL(file2)
// 压缩
return compressImage(file2)
}).then(file3 => {
// 更新预览图片
document.querySelector('img').src = window.URL.createObjectURL(file3)
// 上传
return uploadFile(file3)
}).then(data => {
console.log('上传成功')
}).catch(error => {
console.error('上传失败')
})
}H5 提供了处理文件的接口,借助画布可以在浏览器中实现复杂的图片处理,本文总结了移动端 H5 上传图片这个场景下的一些图片处理实践,以后遇到类似的需求可作为部分参考。
附小程序实现参考
// 拍照
wx.chooseImage({
sourceType: ["camera"],
success: ({ tempFiles }) => {
const file = tempFiles[0]
// 处理图片
}
});
/**
* 压缩图片
* @param {Object} params
* filePath: String 输入的图片路径
* success: Function 压缩成功时回调,并返回压缩后的新图片路径
* fail: Function 压缩失败时回调
*/
compressImage({ filePath, success, fail }) {
// 获取图片宽高
wx.getImageInfo({
src: filePath,
success: ({ width, height }) => {
const systemInfo = wx.getSystemInfoSync();
const canvasWidth = systemInfo.screenWidth;
const canvasHeight = systemInfo.screenHeight;
// 更新画布尺寸
this.setData({ canvasWidth, canvasHeight })
// 计算缩放比例
const scaleX = canvasWidth / width;
const scaleY = canvasHeight / height;
const scale = Math.min(scaleX, scaleY);
const imageWidth = width * scale;
const imageHeight = height * scale;
// 将缩放后的图片绘制到画布
const ctx = wx.createCanvasContext("hidden-canvas");
let dx = (canvasWidth - imageWidth) / 2;
let dy = (canvasHeight - imageHeight) / 2;
ctx.drawImage(filePath, dx, dy, imageWidth, imageHeight);
ctx.draw(false, () => {
// 导出压缩后的图片到临时文件
wx.canvasToTempFilePath({
canvasId: "hidden-canvas",
width: canvasWidth,
height: canvasHeight,
destWidth: canvasWidth,
destHeight: canvasHeight,
fileType: "jpg",
quality: 0.92,
success: ({ tempFilePath }) => {
// 隐藏画布
this.setData({ canvasWidth: 0, canvasHeight: 0 })
// 压缩完成
success({ tempFilePath });
},
fail: error => {
// 隐藏画布
this.setData({ canvasWidth: 0, canvasHeight: 0 })
fail(error);
}
});
});
},
fail: error => {
fail(error);
}
});
}
/**
* 上传文件
*/
uploadFile({ uploadUrl, filePath, onData, onError }) {
wx.uploadFile({
url: uploadUrl
filePath: filePath,
name: "file",
header: {
Cookie: cookie
},
success: res => {
if (res.statusCode === 200) {
onData(res.data)
} else {
onError(res);
}
},
fail: error => {
onError(error);
}
});
}